Setting up BungeeCord to Link Spigot Servers
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
After you’ve got a Minecraft server up and running with Spigot on Debian and Ubuntu, you may want to connect different servers with different collections of plugins. BungeeCord acts as a proxy between the Minecraft client and the server, and allows simple and easy switching between the Spigot servers. It allows for players to connect to one address, yet also access a wider variety of activities than a single Minecraft server instance.
sudo. If you are not familiar with the sudo command, you can check the
Users and Groups guide.Setting Up Your Linode
For the purposes of this tutorial, you create another Debian or Ubuntu Linode to run BungeeCord. This helps to keep it separate from other servers, and allows you to hide the IP of any back-end services.
Assume that the IP of the Linode you’re going to install BungeeCord on is 203.0.113.0, and there are two Spigot servers, with the IP addresses 203.0.113.112 and 203.0.113.198.
Updating and Installing Prerequisite Software
On the Linode that you plan to host BungeeCord:
Update the system:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgradeIf not previously installed, you need to install OpenJDK JRE, an open source Java environment:
sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jre-headlessInstall GNU Screen. This allows BungeeCord to run in the background, even when you are not connected to SSH.
sudo apt-get install screenCreate another user for the BungeeCord proxy, so that it doesn’t have the same privileges as the user. You need to save this password for future reference.
sudo adduser bungeecord
Configuring the Firewall on the BungeeCord Node
If you’re using iptables or ufw to act as a firewall, you’ll need to make a rule on the Linode running BungeeCord. To permit TCP on port 25565 run:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 25565 -j ACCEPT
Configuring the Firewall on the Spigot Server Linodes
For BungeeCord, the Spigot servers need to be in offline mode, as the BungeeCord proxy handles the authentication. This can make the servers vulnerable to people connecting directly, as they can connect with any username, potentially allowing for connection as a user with administrative permissions. To prevent this, you can set up iptables to limit connections to only the BungeeCord server.
Delete existing rules and then allow SSH. If you’ve changed your SSH port, make sure to change the port number
22in the following command:sudo iptables -F sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPTLimit the connections on port 25565 (TCP) to the IP of the BungeeCord Linode,
203.0.113.0. You need to change this for your system:sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s `203.0.113.0` --dport 25565 -j ACCEPTNote If you’re running other Spigot servers on the same Linode, then you need to run step 2 again, but changing25565to the port of the other servers.Allow loopback traffic through the firewall:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPTAllow outgoing connections, and then drop all other packets:
sudo iptables -I INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A INPUT -j DROPNote If you’ve configured youriptablesfirewall by following the Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance tutorial, then you need to append the exceptions in steps 1, 2 and 3 to/etc/iptables.firewall.rulesto ensure that they’re persistent between reboots.
Installing BungeeCord
Log into the BungeeCord Linode as the bungeecord user created earlier, and download BungeeCord:
wget -O BungeeCord.jar http://ci.md-5.net/job/BungeeCord/lastSuccessfulBuild/artifact/bootstrap/target/BungeeCord.jar
Setting up BungeeCord
Start BungeeCord up, allowing it to generate the configuration files:
java -jar BungeeCord.jarAfter the prompt
[INFO] Listening on /0.0.0.0:25577is displayed in the console, typeendand press Enter.Edit
config.ymlby replacing the section of the configuration that readshost: 0.0.0.0:25577tohost: 0.0.0.0:25565because this is the default port that the Minecraft Client attempts to connect to.Edit the following block of the configuration, in order to add existing Spigot servers:
- File: config.yml
1 2 3 4 5servers: lobby: address: localhost:25565 restricted: false motd: 'Just another BungeeCord - Forced Host'
For the servers that are specified as examples in the introduction, it would look like:
- File: config.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9servers: lobby: address: 203.0.113.112:25565 restricted: false motd: 'Just another BungeeCord - Forced Host' games: address: 203.0.113.198:25565 restricted: false motd: 'Just another BungeeCord - Forced Host'
Each server block has a label: In the case of the example,
lobbyorgames. These can be any word you want, but it’s important that they are descriptive, because they are used by the players to change servers.So that players can recognize your server more easily in their server list, you can set a custom message. Change the line that reads
motd: 'Just another Bungeecord - Forced Host'and put your custom message between the quotes. You can use Minecraft color codes here.To allow for UUIDs to be correct in the Spigot servers, you should also ensure that you set
ip_forwardtotrue.Finally, you need to set the default server for players who connect. You can do this by replacing the
lobbyin the line that saysdefault_server: lobbywith the label for your server.Save and exit.
Running BungeeCord
Create the file:
- File: /home/bungeecord/bungeestart.sh
1 2 3#!/bin/bash screen -dmS "bungeecord" java -jar BungeeCord.jar
Run
chmod +x bungeestart.sh, to make the file executable.When you want to start your server, run
./bungeestart.sh.To connect to the server console, run:
screen -r bungeecordWhenever you want to detach from the console, press
Control-afollowed byd
Configuring your Spigot servers for BungeeCord
On the Spigot servers, navigate to the Spigot directory and open
spigot.yml.Change
bungeecord: falsetobungeecord: true. Save and exit.Open the
server.propertiesfile.Change
online-mode=truetoonline-mode=false. Save and exit.Restart the Spigot servers.
Switching Between Servers Without Reconnecting
Connect to the BungeeCord address in Minecraft, and run /server name where name is the name you configured in the BungeeCord config.yml file. It’s that simple!
To see who is online on any of the BungeeCord servers that you’ve linked, run:
/glist
How To Setup IP Forwarding In BungeeCord?
To connect with other players and for the servers to securely identify a player’s identity, you need to enable IP forwarding. With default configuration, servers connected to BungeeCord won’t display the IP of the player, instead, it displays the IP of the BungeeCord server. By enabling IP forwarding, we can identify a player’s IP address.
The first step to enable IP forwarding is to locate the config.yml, and ensure that you followed all steps and that ip_forward is set to true.
- File: config.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10servers: lobby: address: localhost:25565 restricted: false motd: 'Just another BungeeCord - Forced Host' games: address: localhost:25565 restricted: false motd: 'Just another BungeeCord - Forced Host' ip_forward : true
Next, ensure that in your spigot.yml file you have set bungeecord to true
- File: config.yml
1 2bungeecord : true player-shuffle : 0
After, you set the right values for bungeecord and ip_forward, restart the Spigot servers to enable IP forwarding.
Troubleshooting
Unable to Connect to Minecraft
If there is an issue connecting, then it’s important to check that the login servers are up. These quite frequently come under attack, so you need to check if you can access other servers. If you can, and you’re using the right version of Minecraft, there are some simple steps that you can follow to isolate the problem:
Check the Ping
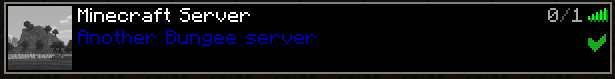
If the server shows the MOTD and a ping in the server list, as in the image, it’s likely that the problem lies between BungeeCord and the Spigot servers. To check, you can log into your BungeeCord server, and you’ll most likely see a line similar to the following in the logs, where the IP 198.51.100.0 is replaced by your IP. This shows that your client is successfully pinging the BungeeCord server:
00:20:34 [INFO] [/198.51.100.0:50677] <-> InitialHandler has connected
If the logs look similar to above, the following error is likely occurring:

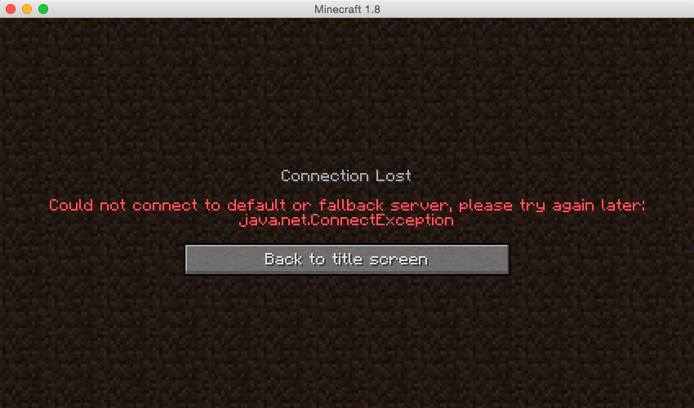
This indicates that Bungee couldn’t contact your Spigot servers. There are a few steps that can help you resolve the issue:
Ensure that the settings in the BungeeCord
config.ymlare correct, especially the server IP addresses and ports. If not, edit them to correct the mistake, and restart BungeeCord.If the settings are correct, then you may want to change the default server to another of the Spigot servers, in case the problem is isolated to the default. Restart BungeeCord.
If the problem continues, then you need to check the Spigot configurations to ensure that you’ve configured them for BungeeCord as detailed above.
If the problem still occurs, it’s likely to be with the firewall on your Spigot servers. You can try running
iptables -Fto clear the rules. You can now test connecting without any firewall, to see if that was causing the issue. As soon as possible after this, you should reconfigure the firewall.
Unable to Ping
In other cases, the server won’t even show a response in the server list:

If this happens, you should check that BungeeCord is actually running, and that you’re attempting to connect to the correct IP address. In this example, it would be 203.0.113.0.
Assuming that the issue is not solved, the issue is likely to be the firewall. You can flush the firewalls using:
iptables -F
You should try again to reconnect. If you can connect now, then you’ll need to reconfigure the firewall.
Reducing Lag In Game By Optimizing spigot.yml
Spigot provides us with a few options to optimize the servers to reduce the lag and optimize performance. In this guide it is illustrated using Minecraft. Here are some Minecraft specific optimizations:
save-user-cache-on-stop-only: The default for this argument is false. This means that it is continuously saving user data, which could potentially lead to heavy performance reduction. You can avoid saving data continuously by setting
save-user-cache-on-stop-onlytotrue, which is its optimized state.entity-activation-range: This argument controls how to activate AI of entities based on how close mobs and entities are to each other. The recommended value for optimization is to keep animals at 16, monsters at 24, raiders at 48, and misc at 8. When you assign these numbers, you define a distance based on blocks for the AI to activate. AI of these entities reactivates when the player is in close proximity again.
merge-radius: When the number of items on the ground ticking is too high, they reduce and significantly induce lag. Optimizing maximum tick time by setting item to 4.0 and exp to 6.0 not only reduces lag but also helps solve issues like items teleporting and showing up in the wrong places.
mob-spawn-range: Another lag-inducing source is if the mobs are spawning at very large distances. When that happens, you have very large active areas. The default value for mob-spawn-range in spigot.yml is 8, which is large. You can optimize the distance from the player at which a mob spawns by setting this value to 6.
item-despawn-rate: You can optimize how fast items dropped to the items despawn. This has a lot of benefits, but the biggest one is on the lag. After you adjust and decrease the default item-despawn-rate from 6,000 to something like 4,000 you get much better performance with significantly reduced lag.
There are other options to optimize spigot.yml that you should check out tick-inactive-villagers, arrow-despawn-rate, and nerf-spawner-mobs.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on